

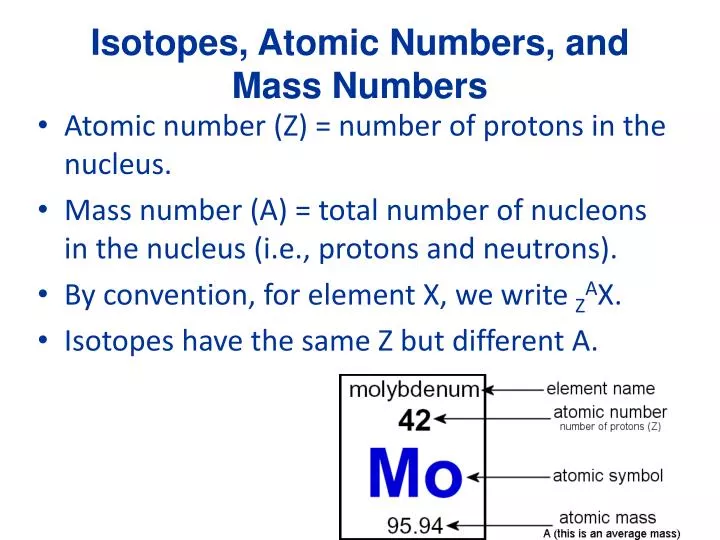
In summary, an atom’s mass number is determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus, while its atomic number is determined by the number of protons. If there are too many neutrons, they can be converted to protons and electrons through beta decay. If there are too many protons in the nucleus, they will repel each other and cause the nucleus to break apart. This is because the strong force, which holds the nucleus together, is balanced by the electromagnetic force, which causes protons to repel each other. Atoms that have too many or too few neutrons relative to their protons can be unstable and undergo radioactive decay. The number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can also affect its stability. However, they may have different physical properties, such as density, melting point, and boiling point, due to their different masses. Isotopes of an element have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons and therefore the same electron configuration. This means that they have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Carbon-14, on the other hand, is present in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is used in radiocarbon dating. Carbon-12 is the most common isotope, accounting for about 98.9% of all carbon atoms, while carbon-13 makes up the remaining 1.1%. Carbon has two stable isotopes – carbon-12 and carbon-13 – and one radioactive isotope – carbon-14. This atom is carbon-13, which is a rare isotope of carbon.

Therefore, there are 7 neutrons in the nucleus of this atom. So, if an atom’s mass number is 13 and its atomic number is 6, we can determine how many neutrons are in its nucleus by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. This is because electrons are so light that their mass is negligible in comparison. The mass of an atom is determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. For example, an atom with six protons is always carbon, while an atom with eight protons is always oxygen. The number of protons in an atom is called its atomic number, which determines the element to which it belongs. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in shells or energy levels. Every atom is made up of three types of particles – protons, neutrons, and electrons. They are the smallest units of an element that can participate in chemical reactions. An Atom’s Mass Number Is 13 And Its Atomic Number Is 6 – How Many Neutrons Are In Its Nucleus?Ītoms are the basic building blocks of matter. An atom with a mass number of 19 and an atomic number of 9 has 10 neutrons in its nucleus. An atom with a mass number of 16 and an atomic number of 8 has 8 neutrons in its nucleus.ĥ. An atom with a mass number of 27 and an atomic number of 13 has 14 neutrons in its nucleus.Ĥ. An atom with a mass number of 14 and an atomic number of 7 has 7 neutrons in its nucleus.ģ. An atom with a mass number of 25 and an atomic number of 12 has 13 neutrons in its nucleus.Ģ. Determining the Number of Neutrons in an Atom’s Nucleus 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
